"Chageyford in the dirt"—The making of Chagford—The old clerk—The church—Tincombe Lane—Chagford Common—Flint finds— Scaur Hill circle—Stone rows—The Tolmen—The Teign river— Camps on it—Drewsteignton cromlech—Gidleigh—Old farmhouses —Fernworthy—The Grey Wethers—Teignhead House—Browne's House—Story about it—Grimspound—Birch Tor stone rows— Chaw Gully—The Webburn.
CHAGFORD is in Domesday written Chageford, and this is the local pronunciation of the name at the present day. The natives say, "Chageford in the dirt—O good Lord!"
But Chagford has had the ability and promptitude to get out of the dirt and prove itself to be anything but a stick-in-the-mud place. It is with places as with people, some have good luck fall to them, others make their fortunes for themselves. Okehampton belongs to the former class, Chagford to the latter. It owes almost everything to a late rector, who, resolved on pushing the place, invited down magazine editors and professional littérateurs entertained them, drove them about, and was rewarded by articles appearing in journals and serials, belauding Chagford for its salubrious climate, its incomparable scenery, its ready hospitality, its rural sweetness, and its archaeological interest.
Whither the writers pointed with their pens, thither the public ran, and Chagford was made. It has now every appliance suitable—pure water, electric lighting, telephone, a bicycle shop, and doctors to patch broken heads and set broken limbs of those upset from the "bikes."
Chagford is undoubtedly a picturesque and pleasant spot. It is situated near Dartmoor, and is sheltered from the cold and from the rainy drift that comes from the south-west. The lodging-house keepers know how to make visitors comfortable, and to charge for so doing. The church has been restored, coaches run to bring visitors, and the roads and lanes have been widened.
I recall the church before modern ideas had penetrated to Chagford. At that time the clerk, who also led the orchestra, gave out the psalm from his seat under the reading-desk, then, whistling the tune, he marched slowly down the nave, ascended to the gallery with leisure, and the performance began.
The church, dedicated to S. Michael, was rebuilt in the middle of the fifteenth century, when the Gorges family owned much land in the parish. Their cognisance, the whirlpool, a canting cognisance (gurges) appears in the bosses of the roof. It contains two monuments of some importance: one is a handsome stone altar tomb, with a canopy supported on columns, in memory of Sir John Whiddon, of Whiddon Park, Judge of Queen's Bench, who died in 1575; the other is to commemorate John Prouze, who died in 1664.
The Three Crowns Inn, opposite the church, is a picturesque building of the seventeenth century. Chagford was one of the Stannary towns, but no remains of the court-house exist.
On Mattadon, above the town, stands a rude early cross of granite.
The ascent to the moor by Tincombe Lane, as I remember it half a century ago, was no better than a watercourse, strewn with boulders, to be scrambled up or down at the risk of dislocation of the ankle. It then well merited the descriptive lines:—
"Tincombe Lane is all uphill
Or downhill, as you take it;
You tumble up, and crack your crown,
Or tumble down and break it.
"Tincombe Lane is crook'd and straight,
Here pothook, there as arrow,
'Tis smooth to foot, 'tis full of rut,
'Tis wide, and then, 'tis narrow.
"Tincombe Lane is just like life,
From when you leave your mother;
'Tis sometimes this, 'tis sometimes that,
'Tis one thing or the other."
Or downhill, as you take it;
You tumble up, and crack your crown,
Or tumble down and break it.
"Tincombe Lane is crook'd and straight,
Here pothook, there as arrow,
'Tis smooth to foot, 'tis full of rut,
'Tis wide, and then, 'tis narrow.
"Tincombe Lane is just like life,
From when you leave your mother;
'Tis sometimes this, 'tis sometimes that,
'Tis one thing or the other."
Now all is changed. A steam-roller goes up and down Tincombe Lane, the angles have been rounded, the precipitous portions made easy, the ruts filled up. And life likewise is now made easy for the rising generation—possibly too easy. Ruggedness had a charm of its own, and bred vigour of constitution and moral physique.
Chagford having lost, by death, the whistling clerk, started a blind organist. Now, also, he is gone. Every peculiarity is being crushed out of modern life by the steam-roller, civilisation.
Chagford Common, as I recall it, half a century ago, was strewn thick with hut circles. One ascended to it by Tincombe Lane and came into a prehistoric world, a Pompeii of a past before Rome was. It was dense with hut circles, pounds, and every sort of relic of the ancient inhabitants of the moor. But inclosures have been made, and but a very few relics of the aboriginal settlement remain. One of the most curious, the "Roundy Pound," only escaped through urgent remonstrance made to spare it. The road carried over the common annually eats up the remains of old, as the road-menders take away the stones from the hut circles to metal the highway.
At Batworthy, one of the inclosures, there must have been anciently a manufactory of flint tools and weapons. Countless spalls of flint and a fine collection of fabricated weapons and tools have been found there, and the collection has been presented from this place to the Plymouth Municipal Museum.
On Gidleigh Common, beside the Teign, opposite Batworthy, is Scaur Hill circle. It consists of thirty-two stones, at present, of which eight are prostrate. The highest of the stones is a little over six feet. The circle is ninety-two feet in diameter. Apparently leading towards this ring, on the Chagford side of the river, was a very long double row of stones, with a second double row or avenue branching from it.
There was a third double row, which started from the Longstone, near Caistor Rock. This Longstone
is still standing, but the stone rows have been
Plan of Stone Rows Near Caster Rock
(Taken in 1851, Scale 1/12 in. to 10 feet.)
A. The Longstone. Hence in a northerly direction the row continued for 520 feet.
B. Cairn. C. Cairn with ring of stones.
In the valley of the Teign is the so-called tolmen, a natural formation. In the same slab or stone may be seen the beginnings of a second hole. But it is curious as showing that the river at one time rolled at a higher elevation than at present. The scenes on a ramble up the river from Chagford to Holy Street Mill and the mill itself are familiar to many, as having furnished subjects for pictures in the Royal Academy.
The river Teign below Whiddon Park winds in and out among wooded precipitous hills to where the Exeter road descends in zigzags to Fingle Bridge, passing on its way Cranbrook Castle, a stone camp. The brook in the name is a corruption of burgh or burrh. On the opposite side of the valley, frowning across at Cranbrook, is Prestonbury Camp.
With advantage the river may be followed down for several miles to Dunsford Bridge, and the opportunity is then obtained of gathering white heath which grows on the slopes. At Shilstone in Drewsteignton is the only cromlech in the county. It is a fine monument. A few years ago it fell, but has been re-erected in its old position. After recent ploughing flints may be picked up in the field where it stands.
Gidleigh merits a visit, the road to it presenting many delicious peeps. Gidleigh possesses the ruin of a doll castle that once belonged to the Prouze family. The church contains a screen in good preservation. In the parish of Throwleigh is the interesting manor house Wanson, of which I have told a story in my Old English Home.
But perhaps more interesting than manor houses are the old farm buildings in the neighbourhood of Chagford, rapidly disappearing or being altered out of recognition to adapt them to serve as lodging-houses to receive visitors.
One such adaptation may be noticed in Tincombe Lane. An old house is passed, where the ancient mullioned windows have been heightened and the floors and ceilings raised, to the lasting injury of the house itself, considered from a picturesque point of view. A passable road leads up the South Teign to Fernworthy, a substantial farm in a singularly lone spot. But there was another farm even more lonely at Assacombe, where a lateral stream descends to the Teign, but it has been abandoned, and consists now of ruin only. Near it is a well-preserved double stone row leading from a cairn and finishing at a blocking-stone.
At Fernworthy itself is a circle of upright stones and the remains of several stone rows sorely mutilated for the construction of a newtake wall. In a tumulus near these monuments was found an urn containing ashes, with a flint knife, and another, very small, of bronze or copper, and a large polished button of horn. On Chagford Common, near Watern Hill, is a double pair of rows leading from a cairn and a small menhir, to blocking - stones. Although the stones of which they are composed are small, the rows are remarkably well preserved.
It will repay the visitor to continue his ascent of the South Teign to the Grey Wethers, two circles of stone, of which, however, many are fallen. Here exploration, such as has been conducted at Fernworthy circle, shows that the floors are deep in ashes, and this leads to the surmise that the circles were the crematories of the dead who lie in the cairns and tunnels in the neighbourhood.
Near the source of the North Teign is Teignhead House, one of the most solitary spots in England. A shepherd resides there, but it is not for many winters that a woman can endure the isolation and retain her reason.
And yet there remain the ruins of a house in a still more lonely situation. The moorman points it out as Browne's House.
Although, judging from the dilapidation and the lichened condition of the stones, one could have supposed that this edifice was of great antiquity, yet it is not so by any means. There are those still alive who remember when the chimney fell; and who had heard of both the building, the occupying, and the destruction of Browne's House. Few indeed have seen the ruin, for it is in so remote a spot that only the shepherd, the rush-cutter, and the occasional fisherman approach it.
On the Ordnance Survey, faint indications of inclosures are given on the spot, but no name is
attached. Yet every moorman, if asked what these
Grimspound, and Entrance
The story told me relative to this solitary spot was that Browne, an ungainly, morose man, had a pretty young wife, of whom he was jealous. He built this place in which to live with her away from the society of men, and the danger such proximity might bring to his connubial happiness.
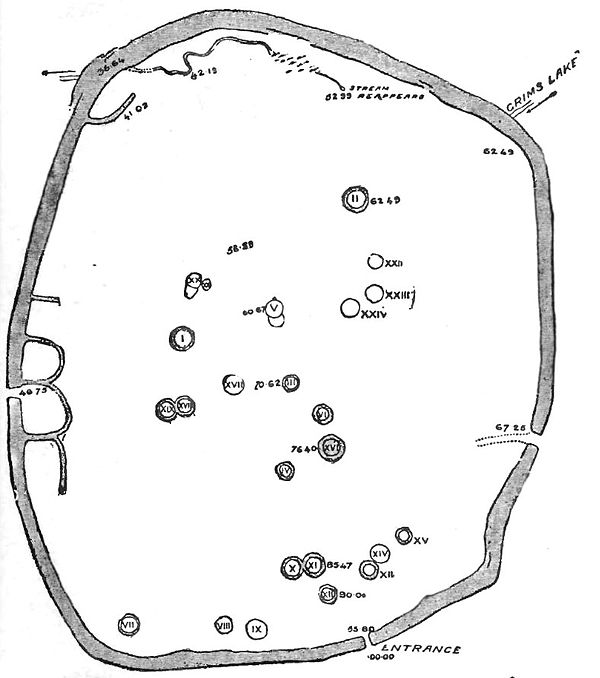
Grimspound will be visited from Chagford. The way to it after leaving the high-road from Post Bridge to Moreton, which it crosses, traverses Shapleigh Common, where are numerous inclosures in connection with hut circles. One of these is very large, and constructed of huge slabs of granite. Several of these larger circles were occupied only in summer, it would appear, as there are scanty traces of fire in them, whereas attached to them are small huts, the floors of which are thickly strewn with charcoal and fragments of pottery, and presumably the cooking was done in these latter.
Grimspound is an irregular circular inclosure containing four acres within the boundary wall. It is situated on the slope of a hill, and the position is obviously ill-adapted for defence, as it is commanded by higher ground on three sides. A little stream, the Grimslake, flows through the inclosure.
The wall itself is double-faced, and the two faces have fallen inwards. This shows that the core could not have been of turf, as in that case shrubs would have rooted themselves therein and have thrust the walls outward. In several places openings appear from the inside of the pound into the space between the walls. It is possible that this intermediate hollow was used for stores, and that the walls were tied together with timber, and surmounted with a parapet of turf. A trackway from Manaton to Headland Warren runs through the pound, and the wall has been broken through for this purpose in two places; but the original entrance to the S.S.E. is perfect, and is paved, and in it three steps have been formed, as the descent was into the pound, another token that the inclosure was not intended as a fortress.
The entrance is 8 feet wide, and no outwork was constructed to protect it from being "rushed" by an enemy. The walls of the inclosure here and throughout are from 10 feet to 12 feet thick, and stone does not exist in any part which could raise them above 5 feet 6 inches in height. Each wall is 3 feet 6 inches wide at base, and was 3 feet at top. On the west side is a huge slab set on edge, measuring 10 feet by 5 feet, and it is from 9 inches to 1 foot in thickness, and weighs from 3 to 4 tons. Other stones, laid in courses, if not so long, are not of less weight. Such a wall as that inclosing Grimspound would cost, with modern appliances and with horse power for drawing the stone, three guineas per land yard, and a land yard would engage four men for a week.
When, moreover, we consider that the circumference of the wall measures over 1,500 feet, it becomes obvious that a large body of men must have been engaged in the erection.
Presumably Grimspound was not a fortified village,
Grimspound
possible, but hardly probable, that it was the place of refuge for the scattered population on Hookner and Hamildon.
Within the pound are twenty-four hut circles; most have been explored, and one (No. III. on the plan) has been partially restored, and is inclosed within a railing. The object of this restoration was to discover, by piling up the stones found in and about the wall of the hut, what its height had been originally, and this was determined to have been four feet.
Unless wantonly injured by trippers, it will serve to exhibit what the structure of these habitations was, with its paved platform as bed, and its hearth and vestibule.
A double hut (XVIII., XIX.) is interesting because a tall stone was erected beside it, as though to indicate it as being the residence of some man of importance, maybe the sheik of the community. In hut XVI. is a double bed, one couch divided from the other by upright stones.
In several of the huts, in the floor, are laid flat stones with a smooth surface, and it was supposed that these served as chopping-stones, but further explorations have led to the belief that they were employed to sustain a central pole that upheld the roof.
On the col above Grimspound, near the source of Grimslake, is a cairn that contains a small kistvaen, and is surrounded by a circle of stones set upright.
Plan of Hut III., Grimspound
been excavated with great labour.
The great central trackway crosses Hamildon, and is very perfect where it does so. It had apparently no connection whatever with Grimspound.
From Grimspound may be seen, on the brow of the ridge connecting Birch Tor and Challacombe Down, a series of stone rows. They lead to a blocking-stone, or menhir, at the south extremity. The northern end has been destroyed by tin- streamers, whose works in Chaw Gully are interesting, for mining has been combined with streaming. The rock has been cut through, but no signs of the use of iron wedges for splitting the granite can here be discovered. It is traditionally told that what was done was to cut a groove in the granite, fill that with quicklime, and pour water on it. The lime in swelling split the rock. Ravens nest here; and I have seen rock doves and the pair of ravens nesting almost side by side.
Below is the Webburn, the stream turned up by tinners. There one mine continues in activity—the "Golden Dagger." Above is Vitifer, where fortunes have been made—and lost; mostly the latter by investors, mainly the former by the "captains" and promoters.
Near Manaton